Bursitis Of The Foot Bursal Cyst
Pain at the posterior heel or posterior ankle is most commonly caused by pathology at the posterior calcaneus, the Achilles (calcaneal) tendon, or the associated bursae. The following bursae are located just superior to the insertion of the Achilles tendon. Subtendinous calcaneal bursa. This bursa (also called the retrocalcaneal bursa), situated anterior (deep) to the Achilles tendon, is located between the Achilles tendon and the calcaneus. Subcutaneous calcaneal bursa. Also called the Achilles bursa, it is found posterior (superficial) to the Achilles tendon, lying between the skin and the posterior aspect of the distal Achilles tendon. Inflammation of one or both of these bursae can cause pain in the posterior heel and ankle regions.
Causes
Inflammation of the bursa causes synovial cells to multiply and thereby increases collagen formation and fluid production. A more permeable capillary membrane allows entrance of high protein fluid. The bursal lining may be replaced by granulation tissue followed by fibrous tissue. The bursa becomes filled with fluid, which is often rich in fibrin, and the fluid can become hemorrhagic. One study suggests that this process may be mediated by cytokines, metalloproteases, and cyclooxygenases.
Symptoms
Achiness or stiffness in the affected joint. Worse pain when you press on or move the joint. A joint that looks red and swollen (especially when the bursae in the knee or elbow are affected). A joint that feels warm to the touch, compared to the unaffected joint, which could be a sign that you have an infection in the bursa. A ?squishy? feeling when you touch the affected part. Symptoms that rapidly reappear after an injury or sharp blow to the affected area.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will check for bursitis by asking questions about your past health and recent activities and by examining the area. If your symptoms are severe or get worse even after treatment, you may need other tests. Your doctor may drain fluid from the bursa through a needle (aspiration) and test it for infection. Or you may need X-rays, an MRI, or an ultrasound.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment for soft tissue conditions focuses on reducing pain and inflammation, and on preserving mobility and preventing disability and recurrence. The treatment for many soft tissue conditions is similar. A doctor's recommendations may include a combination of rest, splints, heat and cold application, medications, physical therapy, or occupational therapy. A person with a soft tissue condition may try several treatments before he or she finds the best one for his or her specific condition.
Prevention
Do not run if you have pain. When you begin running again, avoid running fast uphill or downhill until the tendon is fully healed. Start exercising when caregivers say that it is OK. Slowly start exercise such as bicycling when caregivers say it is OK. When doing exercises that put pressure on the ankles, such as running or walking, exercise on flat, even surfaces. Avoid doing these exercises on very hard surfaces such as asphalt or concrete. Stretch before exercising. Always warm up your muscles and stretch gently before exercising. Do cool down exercises when you are finished. This will loosen your muscles and decrease stress on your heel. Wear heel protectors. Use soft foam or felt heel pads (wedges or cups) to help decrease pressure against your heel. Ask your caregiver which heel pads are the best for you. Wear well-fitting shoes. Buy running or exercise shoes that support and fit your feet well. Do not wear low-cut shoes. Talk to your caregiver or go to a special exercise footwear store to get well-fitting athletic shoes. Ask your caregiver if you should wear specially-made shoe inserts called orthotics (or-THOT-iks). Orthotics can line up your feet in your shoes to help you run, walk and exercise correctly.
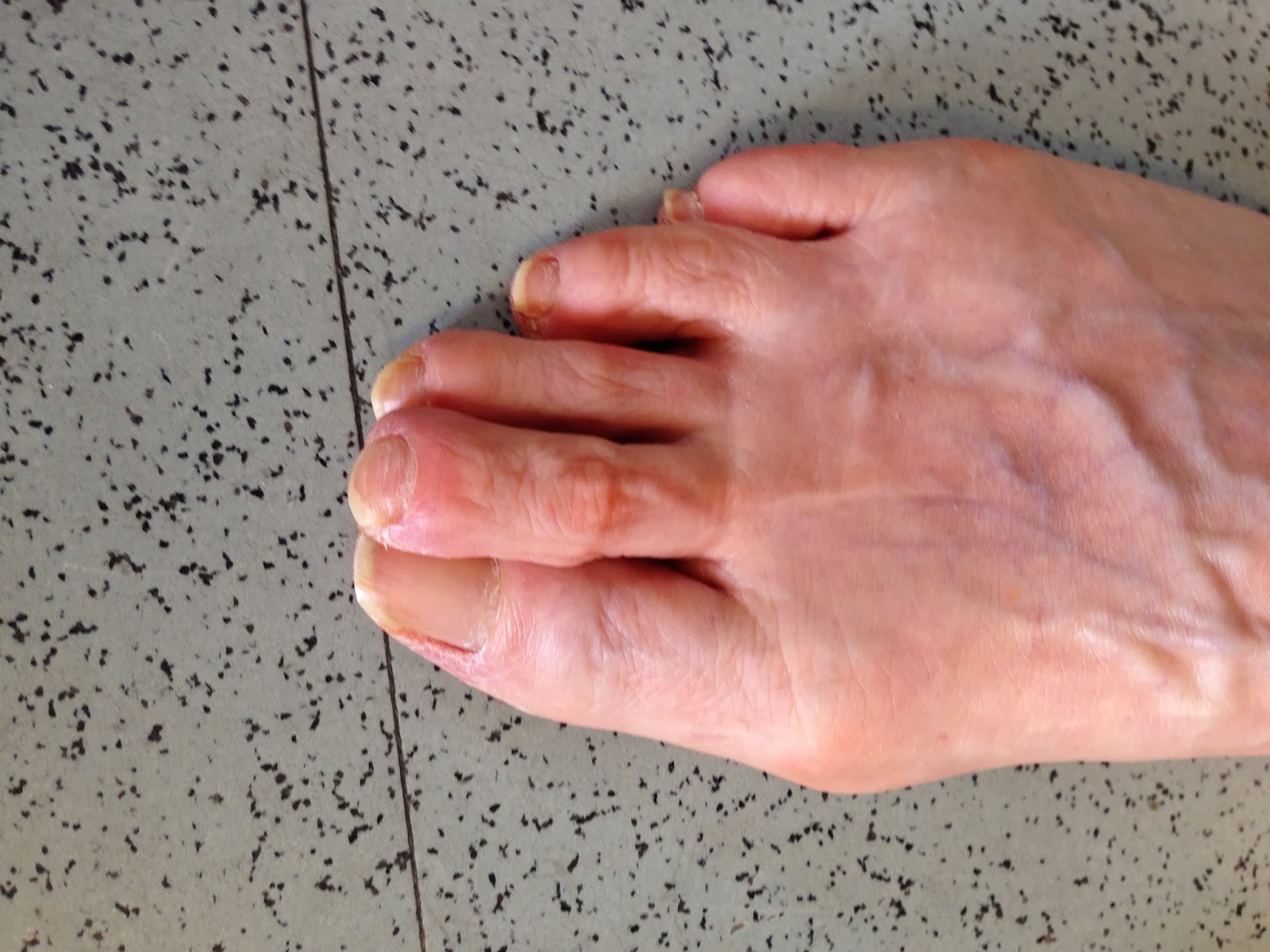
Hammer Toe Cause & Treatment
 Overview
Overview
Hammertoes are another forefoot deformity that can take a walker out of their activity. A Hammer toe generally represent a tendon imbalance in the toes caused by one of the toe tendons getting an advantage over another toe tendon. Most commonly, it is one or all of the long extensor tendons on the top of the foot that gets an advantage over one or all of the flexor tendons on the bottom of the foot, to cause the first joint in the toe to be elevated above the ground. Most shoe wearing people chronically alter the delicate balance that co-exists amongst the toe tendons whether they know it or not.
Causes
The main cause of hammer toe is poorly fitted and/or poorly designed footwear. Any footwear that is too tight in the toe box, especially high-heeled shoes, can push the toes forward, crowding one or more of them into a space that is not large enough to allow the toes to lie flat and spread as they should. Other causes include the following. Changes in foot anatomy. Sometimes the metatarsal bones in the ball of the foot can ?drop,? creating a situation in which hammertoe the toes do not make contact with the surface of the shoe. The toes may then contract at one or both of the joints to re-establish contact with the surface. Traumatic injuries in which toes are jammed or broken. Diabetic neuropathy. This can cause abnormal foot biomechanics due to nerve and/or muscle damage. Damage to nerves and muscles from other conditions, such as arthritis or stroke. Heredity.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
A hammertoe may be present but not always painful unless irritated by shoes. One may have enlarged toe joints with some thickened skin and no redness or swelling. However, if shoes create pressure on the joint, the pain will usually range from pinching and squeezing to sharp and burning. In long standing conditions, the dislocated joints can cause the pain of arthritis.
Diagnosis
Most health care professionals can diagnose hammertoe simply by examining your toes and feet. X-rays of the feet are not needed to diagnose hammertoe, but they may be useful to look for signs of some types of arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis) or other disorders that can cause hammertoe.
Non Surgical Treatment
If the toes are still mobile enough that they are able to stretch out and lay flat, the doctor will likely suggest a change of footwear. In addition, she may choose to treat the pain that may result from the condition. The doctor may prescribe pads to ease the pain of any corns and calluses, and medications ranging from ibuprofen to steroid injections for the inflammation and pain. Other options for non-surgical treatments include orthotic devices to help with the tendon and muscle imbalance or splinting to help realign the toe. Splinting devices come in a variety of shapes and sizes but the purpose of each is the same: to stretch the muscles and tendon and flatten the joint to remove the pain and pressure that comes from corns.
Surgical Treatment
Toes can be surgically realigned and made straight again. They can even be made shorter. The good news is that toes can be corrected. Hammer toe surgery is often synonymous with ?toe shortening?, ?toe job? and/or ?toe augmentation?. Depending on the severity and length of the toe, there are several methods to surgically correct a hammer toe. In general, the surgery involves removing a portion of the bone at the contracted joint, to realign the toe.
 Prevention
Prevention
The best first step you can take is to evaluate your shoe choices. Ditch any shoes that aren?t serving your feet well. Shoes that crowd the front of your foot, especially around your toes, aggravate the existing condition and can also cause the condition to develop. If you suspect the development of hammertoe, you may also try using protective pads to prevent irritation and the development of corns. Custom orthotics to correct muscle imbalances in your feet may also help prevent hammertoe.
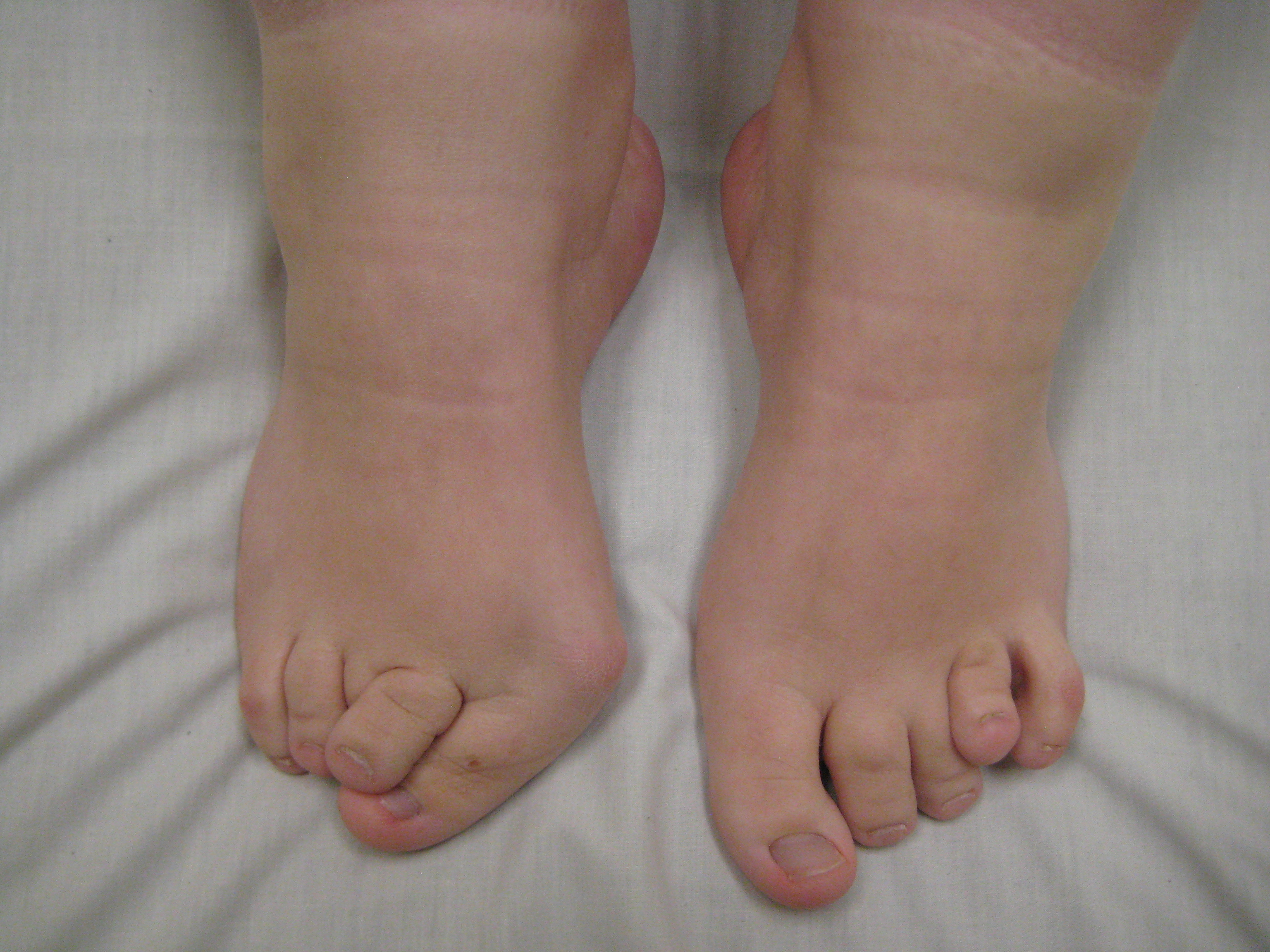
Managing With Bunions
Overview
 A bunion is an abnormal bump, or bony enlargement that forms at the base of your big toe. In the early stages, the bunion may be small and the side of your foot may be slightly swollen. As it progresses, the bump gets larger and becomes increasingly painful. Your big toe may point towards your other toes, rather than straight. Shoes may be uncomfortable to wear and add to the irritation of the joint.
A bunion is an abnormal bump, or bony enlargement that forms at the base of your big toe. In the early stages, the bunion may be small and the side of your foot may be slightly swollen. As it progresses, the bump gets larger and becomes increasingly painful. Your big toe may point towards your other toes, rather than straight. Shoes may be uncomfortable to wear and add to the irritation of the joint.
Causes
Bunions are more common in women than men. The problem can run in families. People born with abnormal bones in their feet are more likely to form a bunion. Wearing narrow-toed, high-heeled shoes may lead to the development of a bunion. The condition may become painful as the bump gets worse. Extra bone and a fluid-filled sac grow at the base of the big toe.
Symptoms
Red, thickened skin along the inside edge of the big toe. A bony bump at this site. Pain over the joint, which pressure from shoes makes worse. Big toe turned toward the other toes and may cross over the second toe.
Diagnosis
X-rays are the best way to determine the amount of deformity of the MTP joint. Blood work may be required to rule out other diseases that may be associated with bunions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Other tests such as bone scans or MRI's are not usually required.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment falls into two broad categories, conservative and surgical. From a conservative standpoint, efforts are directed at correcting faulty foot mechanics with custom molded insoles and relief of symptoms. These include Custom Orthosis to stabilize the abnormal motion of the hind and fore foot. Shoe gear modification: Using shoes with larger toe boxed and more supple materials. Changes in activities. Try to avoid those things which cause symptoms. Anti-inflammatory medication for periodic relief this includes cortisone injections into the joint as well as oral medication. 
Surgical Treatment
If bunions are causing severe foot pain or inflammation and swelling that limits daily activities and doesn't improve with rest, medication and comfortable shoes, surgery may be required. More than 100 surgical options are available for painful bunions. Some realign the foot's anatomy by cutting notches from the metatarsal bone or the bone of the big toe. The bones can then grow back without the slant that promotes bunion growth. The operation is usually done on an outpatient basis, but afterward, you probably will have to stay off your feet for a few weeks. Recovery takes about six weeks. Surgery is not recommended for a bunion that doesn't cause pain.
Is Overpronation
Over-pronation is very prominent in people who have flexible, flat feet. The framework of the foot begins to collapse, causing the foot to flatten and adding additional stress to other parts of the foot. Therefore over-pronation can often lead to a case of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Metatarsalgia, Post-tib Tendonitis and/or Bunions. There are many causes of flat feet. Obesity, pregnancy or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to over-pronation. People with flat feet often do not experience discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all. However, when symptoms develop and become painful, walking becomes awkward and causes increased strain on the feet and calves.

Causes
There are many causes of flat feet. Obesity, pregnancy or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to over-pronation. Often people with flat feet do not experience discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all. However, when symptoms develop and become painful, walking becomes awkward and causes increased strain on the feet and calves.
Symptoms
Because pronation is a twisting of the foot, all of the muscles and tendons which run from the leg and ankle into the foot will be twisted. In over-pronation, resulting laxity of the soft tissue structures of the foot and loosened joints cause the bones of the feet shift. When this occurs, the muscles which attach to these bones must also shift, or twist, in order to attach to these bones. The strongest and most important muscles that attach to our foot bones come from our lower leg. So, as these muscles course down the leg and across the ankle, they must twist to maintain their proper attachments in the foot. Injuries due to poor biomechanics and twisting of these muscles due to over-pronation include: shin splints, Achilles Tendonitis, generalized tendonitis, fatigue, muscle aches and pains, cramps, ankle sprains, and loss of muscular efficiency (reducing walking and running speed and endurance). Foot problems due to over-pronation include: bunions, heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, fallen and painful arches, hammer toes, and calluses.
Diagnosis
One of the easiest ways to determine if you overpronate is to look at the bottom of your shoes. Overpronation causes disproportionate wear on the inner side of the shoe. Another way to tell if you might overpronate is to have someone look at the back of your legs and feet, while you are standing. The Achilles tendon runs from the calf muscle to the heel bone, and is visible at the back of the ankle. Normally it runs in a straight line down to the heel. An indication of overpronation is if the tendon is angled to the outside of the foot, and the bone on the inner ankle appears to be more prominent than the outer anklebone. There might also be a bulge visible on the inside of the foot when standing normally. A third home diagnostic test is called the ?wet test?. Wet your foot and stand on a surface that will show an imprint, such as construction paper, or a sidewalk. You overpronate if the imprint shows a complete impression of your foot (as opposed to there being a space where your arch did not touch the ground).
Non Surgical Treatment
When you see the doctor, he or she will likely perform a complete examination of your feet and watch you walk. The doctor will need to take x-rays to determine the cause of your flat feet. In some cases, further imaging may be needed, especially if your symptoms are severe and sudden in nature. Once you are properly diagnosed, your doctor will create an appropriate treatment plan. There are several options to correct overpronation, such as orthotics. In many cases, overpronation can be treated with non-surgical methods and over-the-counter orthotics. In severe cases, however, custom-made orthotics may work better. Orthotics provide arch support and therefore prevent collapse of the arch with weight bearing. They are made of materials such as spongy rubber or hard plastic. Your doctor will also want to examine your footwear to ensure they fit properly and offer enough medial support. Extra support and stability can be achieved with footwear that has a firm heel counter. If you are experiencing pain, you should be able to use over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen to relieve symptoms.
Prevention
Strengthen the glutes to slow down the force of the foot moving too far inward. Most individuals who over-pronate have weak glute muscles and strengthening this area is a must. A simple exercise to strengthen glutes is lateral tube walking across a field/court/room. Place a lateral stretch band around your ankles and move your leg sideways while keeping your feet forward.
Severs Disease The Truth
Sever's disease (calcaneal apophysitis) is a common cause of heel pain, particularly in physically active young people who are about to begin puberty. The cause is uncertain, but it is thought that the long calf bones of the leg grow faster than the surrounding muscle and soft tissue, causing the Achilles tendon to pull uncomfortably tight. Sever?s disease (sometimes called Sever disease) is a common cause of heel pain, particularly in the young and physically active. It usually develops just before puberty. Boys are slightly more prone to this condition than girls. Physiotherapy can help manage the symptoms of Sever?s disease so that the young person can continue to take part in physical activity. Another name for Sever?s disease is calcaneal apophysitis.
Causes
Sever?s disease is directly related to overuse of the bone and tendons in the heel. This can come from playing sports or anything that involves a lot of heel movement. It can be associated with starting a new sport, or the start of a new season. Children who are going through adolescence are also at risk of getting it because the heel bone grows quicker than the leg. Too much weight bearing on the heel can also cause it, as can excessive traction since the bones and tendons are still developing. It occurs more commonly in children who over-pronate, and involves both heels in more than half of patients.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of Sever?s involves pain or tenderness in one or both heels. This pain usually occurs at the back of the heel, but can also extend to the sides and bottom of the heel. A child with Sever?s may also have these common problems. Heel pain with limping, especially after running. Difficulty walking. Discomfort or stiffness in the feet upon awaking. Swelling and redness in the heel. Symptoms are usually worse during or after activity and get better with rest.
Diagnosis
This condition is self limiting, it will go away when the two parts of bony growth join together, this is natural. Unfortunately, Sever's disease can be very painful and limit sport activity of the child while waiting for it to go away, so treatment is often advised to help relieve it. In a few cases of Sever's disease, the treatment is not successful and these children will be restricted in their activity levels until the two growth areas join, usually around the age of 16 years. There are no known long term complications associated with Sever's disease.
Non Surgical Treatment
It is important that those with Sever?s Disease are treated by a medical professional to reduce pain and allow children to continue to participate in sporting activities. The Athlete?s Foot recommends a visit to your local medical professional to be diagnosed correctly and receive specialised care. Symptoms include pain through the back of the heel where the Achilles tendon inserts into the heel bone, pain during activity especially running and jumping and the back of the heel may be tender to touch.
Prevention
Having Sever?s disease does not predispose children or teens to any other condition, nor is it a permanent problem. It is self-limiting, and when treated, the pain and other symptoms will abate within a few weeks. Once the growth plate has finished growing, Sever?s disease will resolve and won?t recur. It is important to continue to treat any underlying foot conditions and to avoid any long periods of inactivity.
Achilles Tendon Rupture Repair Technique
Overview
 The Achilles tendon is an important part of the leg. It is located just behind and above the heel. It joins the heel bone to the calf muscles. Its function is to help in bending the foot downwards at the ankle (this movement is called plantar flexion by doctors). If the Achilles tendon is torn, this is called an Achilles tendon rupture. The tear may be either partial or complete. In a partial tear, the tendon is partly torn but still joined to the calf muscle. With complete tears, the tendon is completely torn so that the connection between the calf muscles and the ankle bone is lost.
The Achilles tendon is an important part of the leg. It is located just behind and above the heel. It joins the heel bone to the calf muscles. Its function is to help in bending the foot downwards at the ankle (this movement is called plantar flexion by doctors). If the Achilles tendon is torn, this is called an Achilles tendon rupture. The tear may be either partial or complete. In a partial tear, the tendon is partly torn but still joined to the calf muscle. With complete tears, the tendon is completely torn so that the connection between the calf muscles and the ankle bone is lost.
Causes
Repeated stress from a variety of causes is often the cause of Achilles tendon injury. The stress may occur from any of the following. Excessive activity or overuse. Flat feet. Poorly fitting or inadequate shoes. Inadequate warm-up or proper conditioning. Jogging or running on hard surfaces. Older recreational athlete. Previous Achilles tendon injury (tendonitis/rupture). Repeated steroid injections. Sudden changes in intensity of exercise. Use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics (especially in children). Trauma to the ankle. Tense calf muscles prior to exercise. Weak calf muscles.
Symptoms
The classic sign of an Achilles' tendon rupture is a short sharp pain in the Achilles' area, which is sometimes accompanied by a snapping sound as the tendon ruptures. The pain usually subsides relatively quickly into an aching sensation. Other signs that are likely to be present subsequent to a rupture are the inability to stand on tiptoe, inability to push the foot off the ground properly resulting in a flat footed walk. With complete tears it may be possible to feel the two ends of tendon where it has snapped, however swelling to the area may mean this is impossible.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made mostly by clinical examination with a defect usually noted on visual examination and by touching the area. A simple test can be done by squeezing the back of the calf with the foot resting in the air. Normally when squeezing the muscle belly the tendon will shorten causing the foot to move in a downward position. With a rupture this squeezing effect may show no movement of the foot if it is not attached properly. A negative test does not mean there isn't some degree of rupture as some of the tendon fibers may still be attached. Sometimes x-rays, an mri, or an ultrasound can be helpful in determining the extent of the rupture.
Non Surgical Treatment
The treatments of Achilles tendonitis include resting the painful Achilles tendon will allow the inflammation to subside and allow for healing. A period of rest after the onset of symptoms is important in controlling Achilles tendonitis. In patients who have more significant symptoms, a period of immobilization can help. Either a removable walking boot or a cast can allow the inflamed tendon to cool down quickly. A heel wedge can be inserted into the shoe to minimize the stress on the Achilles tendon. These can be placed in both athletic and work shoes. Applying ice to the area of inflammation can help stimulate blood flow to the area and relieve the pain associated with inflammation. Apply ice several times a day, including after exercise. The pain and swelling most commonly associated with Achilles tendonitis can be improved with non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) which include Celebrex?, Advil?, Motrin?, Naprosyn?. Be sure to consult your physician before starting any medications. Physical therapists can help formulate a stretching and rehabilitation program to improve flexibility of the Achilles tendon. Cortisone injections should not be used for Achilles tendonitis. Studies have shown an increased incidence of Achilles tendon rupture after cortisone injections. 
Surgical Treatment
Surgery offers important potential benefits. Besides decreasing the likelihood of re-rupturing the Achilles tendon, surgery often increases the patient?s push-off strength and improves muscle function and movement of the ankle. Various surgical techniques are available to repair the rupture. The surgeon will select the procedure best suited to the patient. Following surgery, the foot and ankle are initially immobilized in a cast or walking boot. The surgeon will determine when the patient can begin weightbearing. Complications such as incision-healing difficulties, re-rupture of the tendon, or nerve pain can arise after surgery. Whether an Achilles tendon rupture is treated surgically or non-surgically, physical therapy is an important component of the healing process. Physical therapy involves exercises that strengthen the muscles and improve the range of motion of the foot and ankle.
Prevention
Achilles tendon rupture can be prevented by avoiding chronic injury to the Achilles tendon (i.e. tendonitis), as well as being careful to warm up and stretch properly before physical activity. Additionally, be sure to use properly fitting equipment (e.g. running shoes) and correct training techniques to avoid this problem!
Functional Leg Length Discrepancy Pelvic Obliquity
Lengthening is usually done by corticotomy and gradual distraction. This technique can result in lengthenings of 25% or more, but typically lengthening of 15%, or about 6 cm, is recommended. The limits of lengthening depend on patient tolerance, bony consolidation, maintenance of range of motion, and stability of the joints above and below the lengthened limb. Numerous fixation devices are available, such as the ring fixator with fine wires, monolateral fixator with half pins, or a hybrid frame. The choice of fixation device depends on the desired goal. A monolateral device is easier to apply and better tolerated by the patient. The disadvantages of monolateral fixation devices include the limitation of the degree of angular correction that can concurrently be obtained; the cantilever effect on the pins, which may result in angular deformity, especially when lengthening the femur in large patients; and the difficulty in making adjustments without placing new pins. Monolateral fixators appear to have a similar success rate as circular fixators, especially with more modest lengthenings (20%).

Causes
Sometimes the cause of LLD is unknown, yet the pattern or combination of conditions is consistent with a certain abnormality. Examples include underdevelopment of the inner or outer side of the leg (hemimelias) or (partial) inhibition of growth of one side of the body of unknown cause (hemihypertrophy). These conditions are present at birth, but the limb length difference may be too small to be detected. As the child grows, the LLD increases and becomes more noticeable. In hemimelia, one of the two bones between the knee and the ankle (tibia or fibula) is abnormally short. There also may be associated foot or knee abnormalities. Hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are rare conditions in which there is a difference in length of both the arm and leg on only one side of the body. There may also be a difference between the two sides of the face. Sometimes no cause can be found. This type of limb length is called idiopathic. While there is a cause, it cannot be determined using currect diagnostic methods.
Symptoms
Children whose limbs vary in length often experience difficulty using their arms or legs. They might have difficulty walking or using both arms to engage in everyday activities.
Diagnosis
Infants, children or adolescents suspected of having a limb-length condition should receive an evaluation at the first sign of difficulty in using their arms or legs. In many cases, signs are subtle and only noticeable in certain situations, such as when buying clothing or playing sports. Proper initial assessments by qualified pediatric orthopedic providers can reduce the likelihood of long-term complications and increase the likelihood that less invasive management will be effective. In most cases, very mild limb length discrepancies require no formal treatment at all.
Non Surgical Treatment
Structural leg length discrepancy can be treated with a heel lift in the shorter leg?s shoe, if the leg length is greater than 5 mm. The use and size of the heel lift is determined by a physical therapist based on how much lift is needed to restore proper lumbopelvic biomechanics. In certain cases, surgical intervention may be needed to either shorten or lengthen the limb. An important component to any surgical procedure to correct leg length discrepancies is physical therapy. Physical therapy helps to stretch muscles and maintain joint flexibility, which is essential in the healing process. For a functional leg length discrepancy no heel lift is required, but proper manual therapy techniques and specific therapeutic exercise is needed to treat and normalize pelvic and lower extremity compensations. The number of treatments needed to hold the pelvis in a symmetrical position is different for each patient based on their presentation and biomechanical dysfunctions in their lower back, pelvis, hip, knee, and foot/ankle. If you have pain in your lower back or lower extremity and possibly a length discrepancy; the two symptoms could be related. A good place to start would be a physical therapy evaluation to determine whether you have a leg length discrepancy and if it could be contributing to your lower back pain, hip pain, knee pain, or leg pain.

Surgical Treatment
Your child will be given general anesthetic. We cut the bone and insert metal pins above and below the cut. A metal frame is attached to the pins to support the leg. Over weeks and months, the metal device is adjusted to gradually pull the bone apart to create space between the ends of the bones. New bone forms to fill in the space, extending the length of the bone. Once the lengthening process is completed and the bones have healed, your child will require one more short operation to remove the lengthening device. We will see your child regularly to monitor the leg and adjust the metal lengthening device. We may also refer your child to a physical therapist to ensure that he or she stays mobile and has full range of motion in the leg. Typically, it takes a month of healing for every centimeter that the leg is lengthened.