Mortons Neuroma Overview
Overview
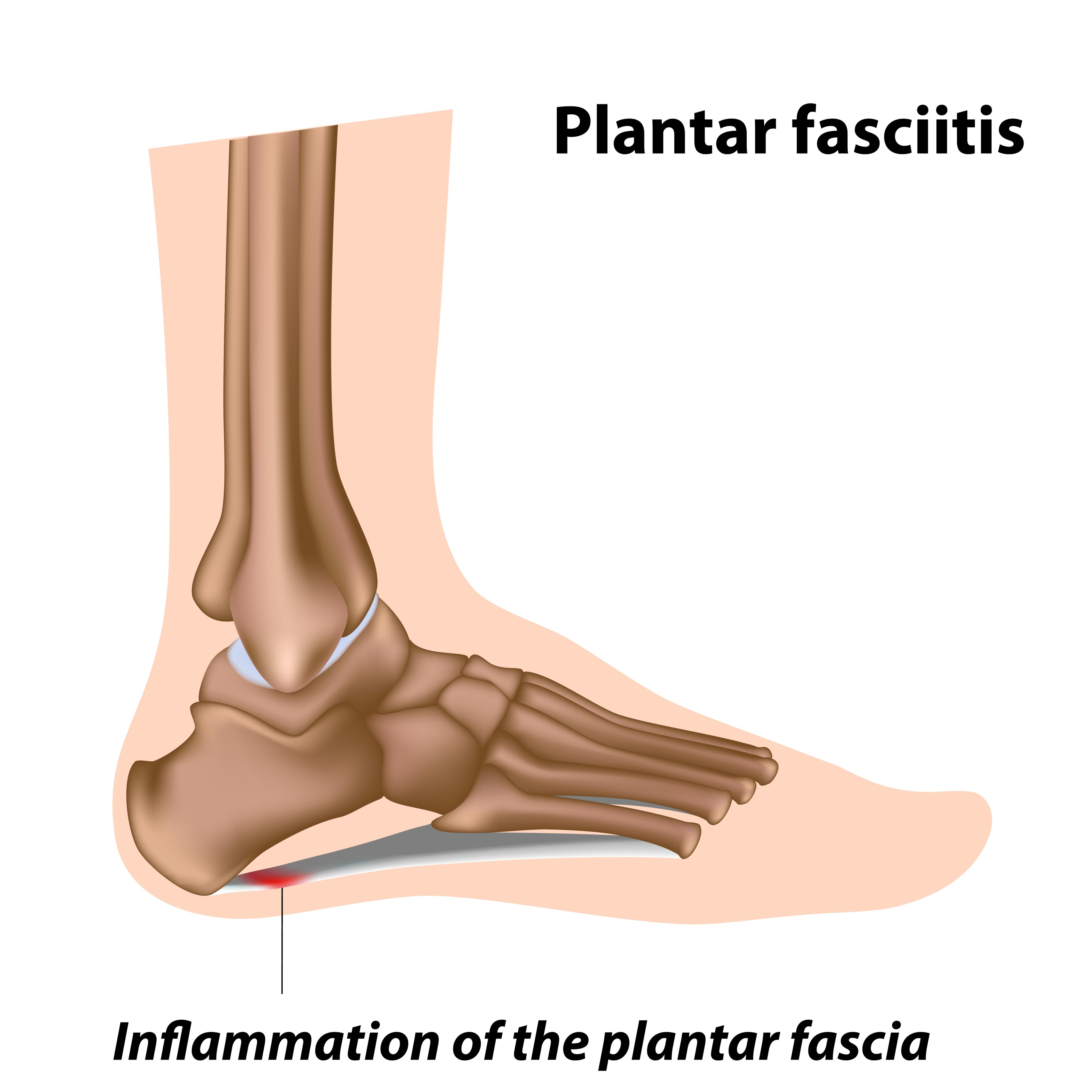 Morton?s Neuroma is a pathological condition of the common digital nerve in the foot, most frequently between the third and fourth metatarsals (third inter-metatarsal space). The nerve sheath becomes abnormally thickened with fibrous (scar) tissue and the nerve fibres eventually deteriorate.This condition is named for the American surgeon, Thomas George Morton (1835-1903), who first recognised the condition in 1876. Incidentally his father was the dentist who discovered the anaesthetics; initially Nitrous oxide, the very gas used today in cryosurgery for the condition his son lent his name to? Morton?s neuroma.
Morton?s Neuroma is a pathological condition of the common digital nerve in the foot, most frequently between the third and fourth metatarsals (third inter-metatarsal space). The nerve sheath becomes abnormally thickened with fibrous (scar) tissue and the nerve fibres eventually deteriorate.This condition is named for the American surgeon, Thomas George Morton (1835-1903), who first recognised the condition in 1876. Incidentally his father was the dentist who discovered the anaesthetics; initially Nitrous oxide, the very gas used today in cryosurgery for the condition his son lent his name to? Morton?s neuroma.
Causes
Morton's neuroma is an inflammation caused by a buildup of fibrous tissue on the outer coating of nerves. This fibrous buildup is a reaction to the irritation resulting from nearby bones and ligaments rubbing against the nerves. Irritation can be caused by Wearing shoes that are too tight. Wearing shoes that place the foot in an awkward position, such as high heels. A foot that is mechanically unstable. Repetitive trauma to the foot such as from sports activities like tennis, basketball, and running. Trauma to the foot caused by an injury such as a sprain or fracture. It is unusual for more than one Morton's neuroma to occur on one foot at the same time. It is rare for Morton's neuroma to occur on both feet at the same time.
Symptoms
People with Morton's neuroma usually complain of pain that can start in the ball of the foot and shoot into the affected toes. However, some people just have toe pain. There may also be burning and tingling of the toes. The symptoms are usually felt up the sides of the space between two toes. For example, if the nerve between the third and fourth long bones (metatarsals) of the right foot is affected, the symptoms will usually be felt up the right-hand side of the fourth toe and up the left-hand side of the third toe. Some people describe the pain that they feel as being like walking on a stone or a marble. Symptoms can be made worse if you wear high-heeled shoes. The pain is relieved by taking your shoe off, resting your foot and massaging the area. You may also experience some numbness between the affected toes. Your affected toes may also appear to be spread apart, which doctors refer to as the 'V sign'. The symptoms can vary and may come and go over a number of years. For example, some people may experience two attacks of pain in a week and then nothing for a year. Others may have regular and persistent (chronic) pain.
Diagnosis
To diagnose Morton's neuroma the podiatrist commonly palpates the area to elicit pain, squeezing the toes from the side. Next he or she may try to feel the neuroma by pressing a thumb into the third interspace. The podiatrist then tries to elicit Mulder's sign, by palpating the affected interspace with one hand and squeezing the entire foot at the same time with the other hand. In many cases of Morton's neuroma, this causes an audible click, known as Mulder's sign. An x-ray should be taken to ensure that there is not a fracture. X-rays also can be used to examine the joints and bone density, ruling out arthritis (particularly rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis).
Non Surgical Treatment
Most non-operative treatment is usually successful, although it can take a while to figure out what combination of non-operative treatment works best for each individual patient. Non-operative treatment may include the use of comfort shoe wear. The use of a metatarsal pad to decrease the load through the involved area of the plantar forefoot. A period of activity modification to decrease or eliminate activities, which maybe exacerbating the patient?s symptoms. For example, avoiding long periods of standing or other activities that result in significant repetitive loading to the forefoot can be very helpful. Wearing high heels should be avoided. Local corticosteroid injections can help decrease inflammation associated with the nerve. However, this does not necessarily address the underlying loading forces that maybe causing the injury to the nerve in the first place. It has been proposed that an alcohol injection in and around the nerve will cause a controlled death to the nerve and subsequently eliminate symptoms from the nerve. In theory, this may be helpful. In practice, adequate prospective studies have not demonstrated the benefit of this procedure above and beyond the other standard non-operative treatments available. In addition there is the concern that the alcohol will cause excessive scarring and death of other important structures in the area.
Surgical Treatment
Operative treatment of Morton?s neuroma should be entertained only after failure of non-operative management. Standard operative treatment involves identifying the nerve and cutting (resecting) it proximal to the point where it is irritated/injured. This is usually done through an incision on the top (dorsal) aspect of the foot, although an incision on the sole (plantar) aspect of the foot can be used. Some physicians will attempt to treat Morton?s neuroma by releasing the intermetatarsal ligament, and freeing the nerve of local scar tissue. This may also be beneficial.
 Morton?s Neuroma is a pathological condition of the common digital nerve in the foot, most frequently between the third and fourth metatarsals (third inter-metatarsal space). The nerve sheath becomes abnormally thickened with fibrous (scar) tissue and the nerve fibres eventually deteriorate.This condition is named for the American surgeon, Thomas George Morton (1835-1903), who first recognised the condition in 1876. Incidentally his father was the dentist who discovered the anaesthetics; initially Nitrous oxide, the very gas used today in cryosurgery for the condition his son lent his name to? Morton?s neuroma.
Morton?s Neuroma is a pathological condition of the common digital nerve in the foot, most frequently between the third and fourth metatarsals (third inter-metatarsal space). The nerve sheath becomes abnormally thickened with fibrous (scar) tissue and the nerve fibres eventually deteriorate.This condition is named for the American surgeon, Thomas George Morton (1835-1903), who first recognised the condition in 1876. Incidentally his father was the dentist who discovered the anaesthetics; initially Nitrous oxide, the very gas used today in cryosurgery for the condition his son lent his name to? Morton?s neuroma.Causes
Morton's neuroma is an inflammation caused by a buildup of fibrous tissue on the outer coating of nerves. This fibrous buildup is a reaction to the irritation resulting from nearby bones and ligaments rubbing against the nerves. Irritation can be caused by Wearing shoes that are too tight. Wearing shoes that place the foot in an awkward position, such as high heels. A foot that is mechanically unstable. Repetitive trauma to the foot such as from sports activities like tennis, basketball, and running. Trauma to the foot caused by an injury such as a sprain or fracture. It is unusual for more than one Morton's neuroma to occur on one foot at the same time. It is rare for Morton's neuroma to occur on both feet at the same time.
Symptoms
People with Morton's neuroma usually complain of pain that can start in the ball of the foot and shoot into the affected toes. However, some people just have toe pain. There may also be burning and tingling of the toes. The symptoms are usually felt up the sides of the space between two toes. For example, if the nerve between the third and fourth long bones (metatarsals) of the right foot is affected, the symptoms will usually be felt up the right-hand side of the fourth toe and up the left-hand side of the third toe. Some people describe the pain that they feel as being like walking on a stone or a marble. Symptoms can be made worse if you wear high-heeled shoes. The pain is relieved by taking your shoe off, resting your foot and massaging the area. You may also experience some numbness between the affected toes. Your affected toes may also appear to be spread apart, which doctors refer to as the 'V sign'. The symptoms can vary and may come and go over a number of years. For example, some people may experience two attacks of pain in a week and then nothing for a year. Others may have regular and persistent (chronic) pain.
Diagnosis
To diagnose Morton's neuroma the podiatrist commonly palpates the area to elicit pain, squeezing the toes from the side. Next he or she may try to feel the neuroma by pressing a thumb into the third interspace. The podiatrist then tries to elicit Mulder's sign, by palpating the affected interspace with one hand and squeezing the entire foot at the same time with the other hand. In many cases of Morton's neuroma, this causes an audible click, known as Mulder's sign. An x-ray should be taken to ensure that there is not a fracture. X-rays also can be used to examine the joints and bone density, ruling out arthritis (particularly rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis).
Non Surgical Treatment
Most non-operative treatment is usually successful, although it can take a while to figure out what combination of non-operative treatment works best for each individual patient. Non-operative treatment may include the use of comfort shoe wear. The use of a metatarsal pad to decrease the load through the involved area of the plantar forefoot. A period of activity modification to decrease or eliminate activities, which maybe exacerbating the patient?s symptoms. For example, avoiding long periods of standing or other activities that result in significant repetitive loading to the forefoot can be very helpful. Wearing high heels should be avoided. Local corticosteroid injections can help decrease inflammation associated with the nerve. However, this does not necessarily address the underlying loading forces that maybe causing the injury to the nerve in the first place. It has been proposed that an alcohol injection in and around the nerve will cause a controlled death to the nerve and subsequently eliminate symptoms from the nerve. In theory, this may be helpful. In practice, adequate prospective studies have not demonstrated the benefit of this procedure above and beyond the other standard non-operative treatments available. In addition there is the concern that the alcohol will cause excessive scarring and death of other important structures in the area.

Surgical Treatment
Operative treatment of Morton?s neuroma should be entertained only after failure of non-operative management. Standard operative treatment involves identifying the nerve and cutting (resecting) it proximal to the point where it is irritated/injured. This is usually done through an incision on the top (dorsal) aspect of the foot, although an incision on the sole (plantar) aspect of the foot can be used. Some physicians will attempt to treat Morton?s neuroma by releasing the intermetatarsal ligament, and freeing the nerve of local scar tissue. This may also be beneficial.